Is Your Website Hacked or Infected? Find out Ways to Verify & Tips to Clean Your Hacked Website
Recently updated: March 16th, 2020
Every 39 seconds a hacker’s attack occurs, while 30,000 new websites are hacked every day (as per reports shared by Clark School, University of Maryland and SophosLab, respectively). This is indeed an alarming number. Finding out about your ‘hacked website’ too late is catastrophic because you have gifted enough time to the hackers to infect and do the intended damage to your website.
That’s why you often need to ask yourself a bunch of questions about your website security, such as:
- Is my website secured?
- Is my website hacked?
- How to recover my website from hacking?
- What to do when my website is hacked?
- How to clean my website?
Keeping your website safe from hackers is like an ongoing battle. Lowering the guards means you are putting your website at risk.
To help you keep your website secured, here, we are going to discuss three vital topics:
- How to check if a website is hacked
- How to clean a hacked website
- How to secure a website from future hackers’ attacks
If you are also concerned about your website security or a victim of such a cybercrime, read till the end to ensure that your website doesn’t make an easy prey for hackers.
A. How to Check If a Website Is Hacked
There are several ways to detect whether your website has been attacked or not. The most popular and easy-to-try methods are:
A.1. Check “Security Issues” Report of Google Search Console
If you haven’t created an account in Google Search Console, create an account now. For those who have already an account, follow the steps given below:
- First of all, log into your Google Search Console account: https://search.google.com/search-console/welcome.
- Select Security Issues in the “Security & Manual Actions” tab present on the left-hand sidebar.
- View your “Security Issues” Report and analyze it.
Here is a screenshot of what this report may look like if you have security issues.
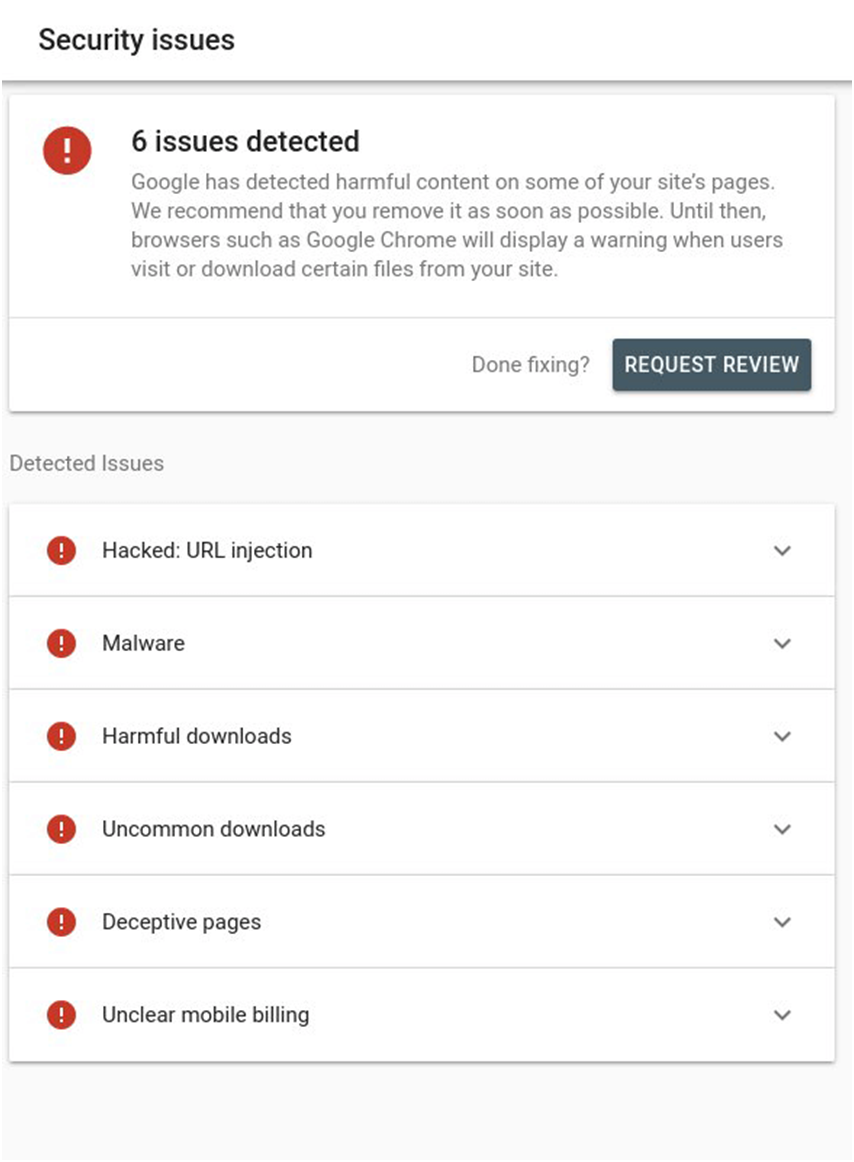
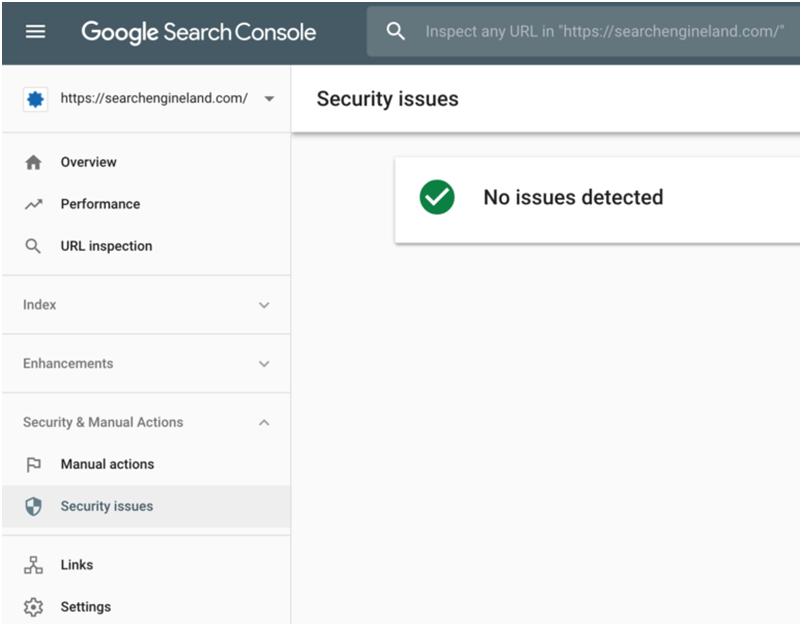
In case, there is no security threat, you will see something like this:
The reports include all issues, if any, found in your website, including:
- Malware warnings
- Phishing attempt
- Deceptive pages
- Code and content injections
- URL injections
- SQL injections
- Harmful downloads
Start working out if your website’s security issues report shows any issue to be resolved. If your site is hacked, you need to act faster to recover your website as well as protect your website visitors.
Alternatively, you can also find out security issues via reliable site scanners. They will help you find out malicious payloads and malware locations. In case there is none, you should continue to perform other tests available.
Remember that when you have multiple websites on the same server, you should scan and check all of them.
A.2. Check Website Status via Google’s Safe Browsing tool
You can scan your website to see whether your website has been hacked. The Safe Browsing tool offered by Google allows you to instantly check your website’s status.
Google scans sites’ index daily, check for malware issues, and also employ advanced statistical models to locate phishing websites.
Follow these steps to use Google’s Safe Browsing Tool:
- Visit the Google Transparency Report: https://transparencyreport.google.com/safe-browsing/search.
- Enter the URL of your website in the search box.
- Check out the results.
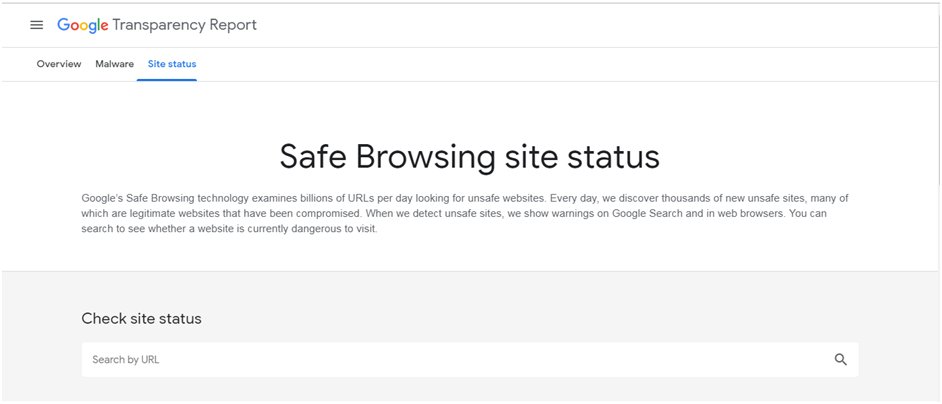
If it shows that your website is hacked or compromised, start to restore your website integrity as early as possible. Once you are done with resolving, check out the status again or recheck your site on Google Search Console.
Google also recommends an alternative of visiting Stop adware and making a website review request if your website is listed as bad by many search engines.
Besides, you can also submit a review request in your Google Search Console (formerly known as Google Webmaster Tools) dashboard. Google will assess and mark your site as safe within 24 hours if the reported issues are resolved already.
A.3. Check out the Core File Integrity and Recently Modified Files
Most core files are not meant to be modified and therefore, you should keep these files under your radar for modifications. Important site files, such as .htaccess and .php files can also inform you about hacking. You or your team of developers can look for malicious code and unsecure links created by hackers.
For developers, the fastest way to verify the integrity of your website core files is to use the diff command in the terminal. If not familiar with it, you can also manually verify files through SFTP. If no modification is found, core files are clean.
See whether there are any recently modified files to detect hacking. You can use following terminal commands on Linux:
Type in the terminal:
$ find /etc -type f -printf ‘%TY-%Tm-%Td %TT %p\n’ | sort -r .
To check directory files, type in the terminal:
$ find /etc -printf ‘%TY-%Tm-%Td %TT %p\n’ | sort -r .
In case there are unknown modifications within the last 30 days, it is an indication of suspicious activity.
If you don’t understand this, don’t worry. You can use other discussed methods in this post to detect hacking.
A.4. Keep an eye on notifications sent by hosting providers and browsers
If your website is hacked, you may also be notified by:
- Hosting Provider
- Internet Browser
- Google Search Console
- Internet User Site-Scanner
With a reliable hosting provider, for instance, GoDaddy or HostGator, you will receive notifications about hacking. In most cases, hosting providers take the hacked or infected website offline and alert the website owner via email.
Besides, you may also be alerted by Google via a red screen that warns you are visiting a harmful or hacked website. You may also receive security alerts from Google Search Console and emails about security issues found and manual actions based on the settings.
When it comes to detecting cyber attacks, you can also download a popular malware scanner, such as ‘IsItWP’ WordPress scanner, to catch the security issues.
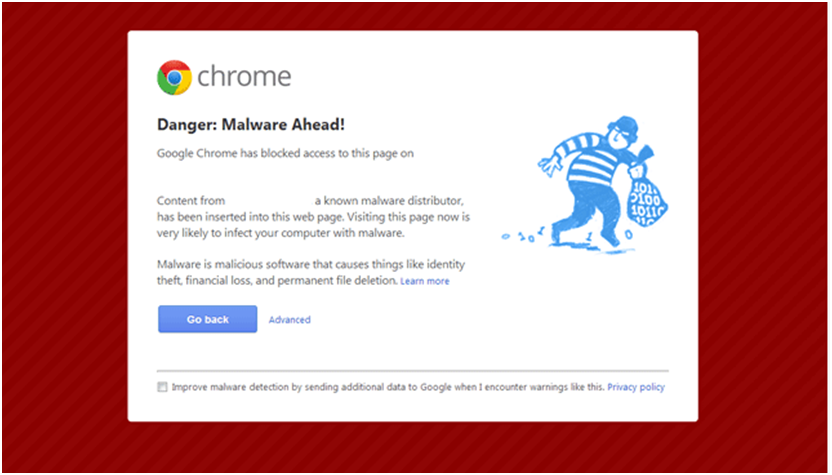
When it is about protecting your website from hackers and cyber attacks, keep an eagle eye for notifications because the sooner you find out, the better and faster you can recover.
A.5. Check out Google Search Results – the easiest way to discover a hacked website
Aforementioned, Google daily scans the index of websites. When Google finds out ‘a website is hacked’, it displays the message ‘this site may harm your computer’ or ‘this site is hacked’ in search results as well.
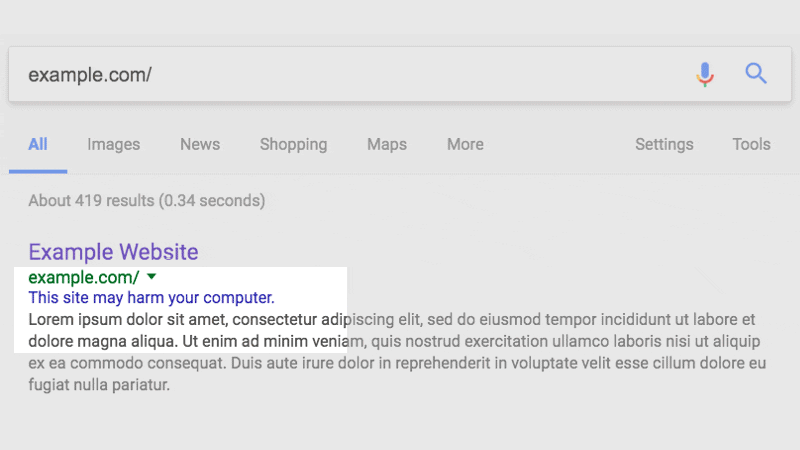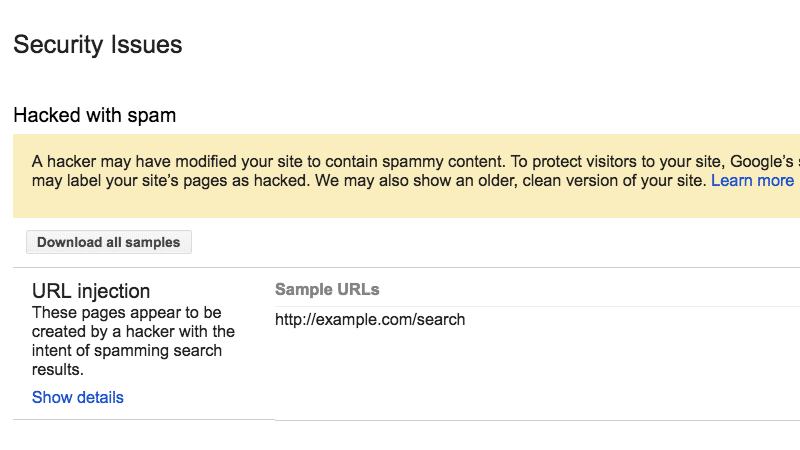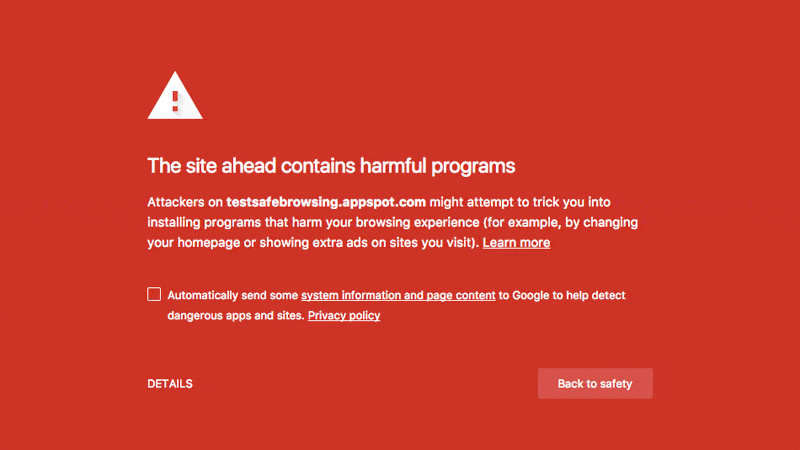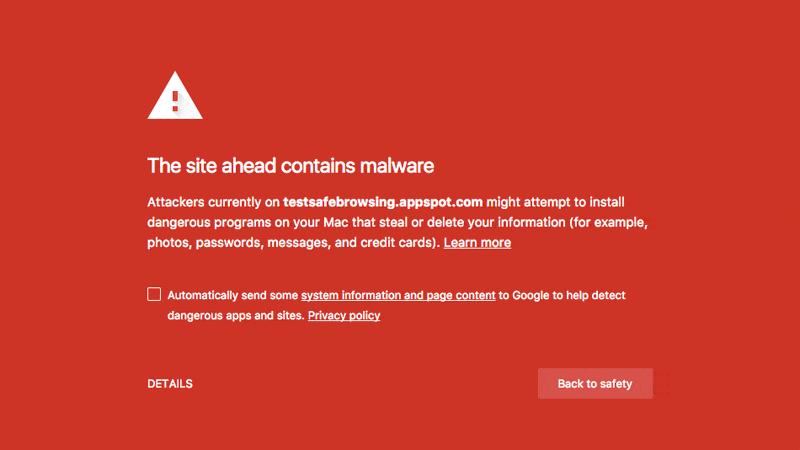
Fix the issue when you see this or a similar message. Once you have fixed it, submit a review request to Google Search Console to verify your website integrity.
A.6. Verify your website security via Google’s Hacked Sites Troubleshooter
This tool is suitable when you are having trouble in locating:
- Entire hacked content on your website
- Double-check after cleaning up your website
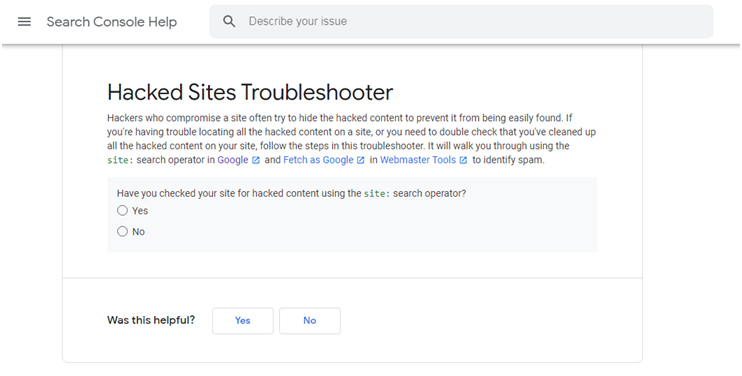
Hacked Sites Troubleshooter is a free tool offered by Google to expose the hackers who try to hide the hacked content to prevent it from being detected.
B. How to clean a hacked website
Cleaning websites early after finding out about hacking issues is extremely essential to prevent further damage.
You can take the following approaches when it comes to fixing a hacked website:
- In-House Support – Leverage your in-house team to analyze the condition and fix the website.
- Outsourcing – Seek the assistance of a third party to remove the malicious code and repair your site.
Remember that each hacking attempt or attack is different and you can’t follow the same solution or fixing method to recover your website.
However, some methods might help in website recovery from hacking attacks.
First, compare the current state of your website with an old and clean backup if available. It will help you spot the modifications made recently.
B.1. Clean your website hacked files
When you have a recent clean backup, you can replace infected files easily.
For manual removal of infected files from your website, follow these steps:
- Log into your server with SFTP or SSH.
- Create a new backup before making any changes.
- Locate the recently modified files and confirm the date of modifications introduced by the user.
- Open the suspicious files.
- Open custom or premium files with a text editor and remove suspicious code.
- Perform a test to check if the website is still functional.
B.2. Clean your website’s hacked database tables
Connect to the database through the database admin panel to remove a malware infection from your websites’ database.
To manually clean your database, perform the steps mentioned below:
- Log into the database admin panel to connect with the database.
- Create a fresh backup before introducing any changes.
- Find out spammy keywords, links, or other suspicious content.
- Open the table with suspicious content.
- Manually delete the suspicious content.
- Test to check if the database is still operational.
- Remove all database access tools you may have uploaded.
Beginners can refer to the information provided by malware scanners or other tools, while intermediate users can look for harmful PHP functions, such as eval, preg_replace, str_replace, base64_decode, move-uploaded-file, etc.
Before making any changes, remember that these functions may also be used by plugins legitimately. So, be sure, before deleting any function.
B.3. Increase the Security for User Accounts
Whenever you notice any unfamiliar user, delete that account immediately. It is highly recommended to assign only one admin and restrict the privileges for other user roles, for instance, contributor, author, and editor. If you need more than one admin, try to keep them fewer.
Besides, also be informed that non-secure usernames and passwords provide hackers and attackers more chances of success.
According to a study conducted by Michel Cukier, Clark School Assistant Professor,
The majority of attacks come from the hackers who use “dictionary scripts” software that use common usernames and passwords to break into the computer.
Top usernames that made to the hacking list are:
- Root
- Admin
- Test
- Guest
- Info
- Adm
- Mysql
- User
- Administrator
- Oracle
Top passwords that are easily guessed by hackers:
- 123456
- Password
- 1234
- 12345
- Passwd
- 123
- Test
- 1
The NCSC also shared a separate analysis of 100,000 commonly used passwords that have been hacked by third parties.
Here is the table shared by NCSC on its website about regularly passwords breached by hackers.
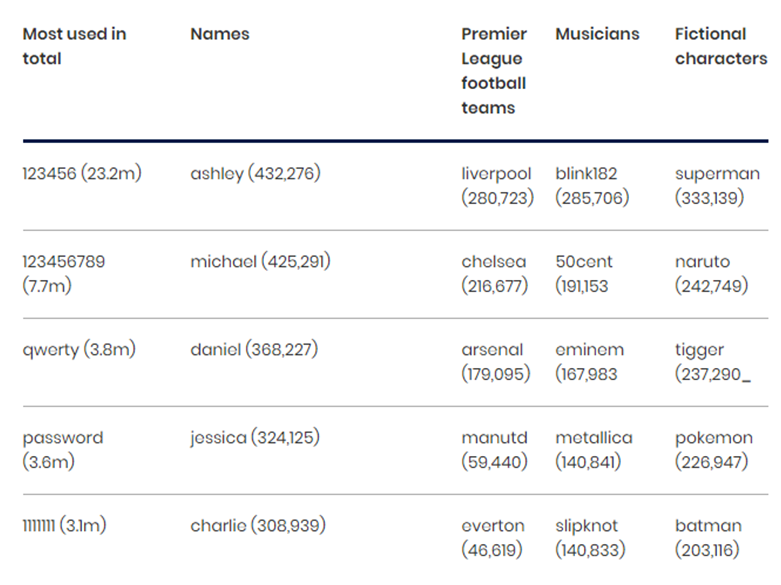
Therefore, create strong, random, hard-to-guess passwords and usernames while creating user and admin accounts.
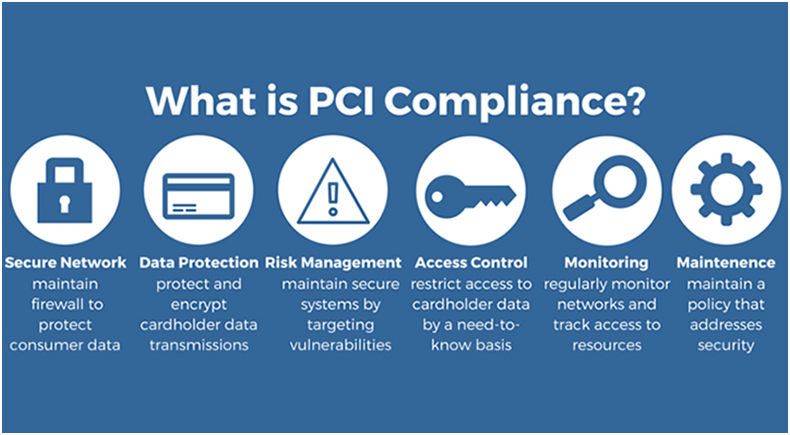
B.4. PCI Considerations for eCommerce Websites
If you have an eCommerce website and payment processing system within your online store, securing consumer credit card data must be your top priority as there is Payment Card Industry (PCI) compliance that you are mandated to follow.
Instantly contact your bank when you suspect credit card data is being stolen and ask about virtual credit cards. You can use them to test purchases on your online store before cleaning your website. While you can investigate the issue on your own in the beginning, you must seek the help from PCI Forensic Investigator (PFI) as soon as you find some evidence to ensure that your customers’ credit card information is safe.
C. How to secure a website from future hackers’ attacks
All of us are well aware of the proverb “Prevention is better than cure”. Apply this to your website security as well.
Secure your website from hackers using the methods mentioned below:
C.1. Stay updated and Reset Configuration Settings
Many times, outdated software is the leading cause of infections. It could be your CMS, themes, plugins, extensions, and other tools and software you use. So, stay updated and informed.

Also, reset potentially compromised credentials to ensure that your website is not infected
Keep in mind to follow these tips:
- Update your website software once new updates are available.
- Reset passwords regularly for all access points, including user account, cPanel, SSH, FTP, SFTP, and database.
- Set privileges of users accordingly.
- Reinstall all plugins and extensions after a hack and remove all deactivated plugins.
C.2. Reduce Entry Points in Your Website
Try to minimize the attack surface or entry points for attackers. A lot of ways are available to harden your website (i.e. reducing entry points) available online.
C.3. Create Backups as Recovery Aide
Create backup after cleaning your website and making necessary modifications. It is also considered a good security practice.
Tips to create a backup for your website:
- Store backups in an offsite location rather than servers.
- Configure your backup solution to create a backup with a frequency that suits your website’s requirements.
- Create backups of your backups as a part of the redundancy backup strategy.
- Test whether your website functions properly at regular intervals.
C.4. Scan Your System
As some infections are targeted to jump from a computer into text editors or FTP clients, you should scan your computer system and have all your website users run a good antivirus program run on their operating systems.

C.5. Defend Your Website with Firewall
As the number of attacks is piling up every day, cybersecurity experts recommend using a website firewall.

It will benefit in several ways, such as:
- Detects and stops known hacking operations
- Patches the hole in your website software
- Stops unauthorized access to your wp-admin and wp-login page
- Detects and blocks Distributed Denial of Service attacks
- Offers to cache to boost page speed
Remember that website security should be one of your topmost concerns as it not only affects your website’s performance but also impacts your brand and your website visitor’s confidentiality. So, always be wary of hackers when you are a part of the digital world.
Latest posts by Vijaya Tyagi (see all)
How To Track Shopify SEO Performance & Metrics (2025) - January 14, 2025
Link Building Strategies: The Ultimate Techniques for 2025 - December 31, 2024

