Crucial SEO Principles 2024: Step-by-Step Guide to Higher Rankings
Recently updated: July 3rd, 2024
Search engines are the source of 93 percent of online experiences. Plus, 60 percent of marketers say that inbound marketing (such as SEO and blog) is their highest quality source of generating qualified leads. This makes SEO essential for every business to increase sales and revenue.
SEO stands for search engine optimization and refers to the process of website optimization using various SEO techniques to rank your website on the top of search engine results in major search engines, such as Google and Bing.
With the help of SEO, you can:
- Improve the online visibility of your business
- Divert organic (free) traffic to your website
- Rank your website in the top positions of Google’s #1 Page
- Enhance brand awareness and reputation
- Build credibility in the eyes of customers
- Attract online users who are interested in what you offer
- Generate more qualified leads
- Improve local presence and drive foot traffic to your physical store
Did You Know?
- The average return on investment (ROI) for e-commerce SEO is 700% or more. (Source)
- 57% of B2B marketers revealed that SEO brings in more leads than other marketing methods. (Source)
- 94% of search engine users ignore paid ads and prefer organic search results (Source)
If you have not invested in SEO, now is the best time to strengthen the SEO of your website and expand your business in terms of brand awareness and customers. To get started with SEO, you must know the core SEO principles to run successful SEO campaigns and achieve your marketing goals.
7 SEO Principles You Must Know to Rank Your Website Higher
1. SEO Principle: Keyword Research and Optimization
1.1. Identifying the Right Keywords
Choosing the right keywords and phrases can make or break your ability to rank higher in search results. With the right SEO approach, keyword optimization can significantly boost your website’s visibility and traffic.
Begin the keyword research by brainstorming a list of terms and phrases related to your business, products, and target audience. Think about the words and questions someone might type into a search engine when looking for what you offer.
To get started, you can also simply type the basic service or general name of your product in Google Search to find related keywords.
Aim for a thorough list of potential keywords, including common terms and specific long-tail keywords.
Long-tail keywords are more targeted phrases and contain 3 to 5 or more words.
Some good examples of long-tail keywords are:
- Organic pillows for neck pain
- Appliance repair in Austin, TX
- Pet food in Dubai, UAE
- Small business accounting software
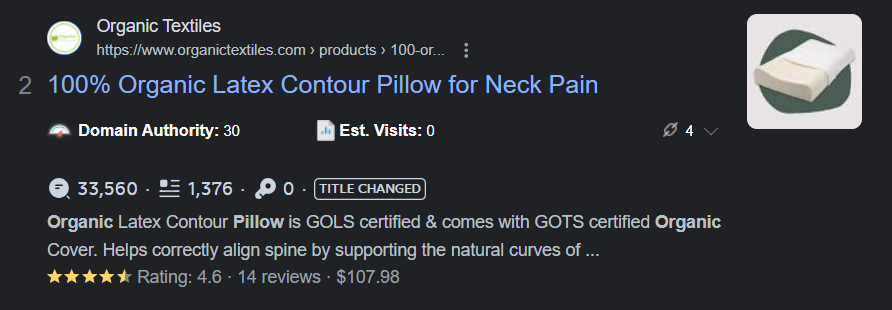
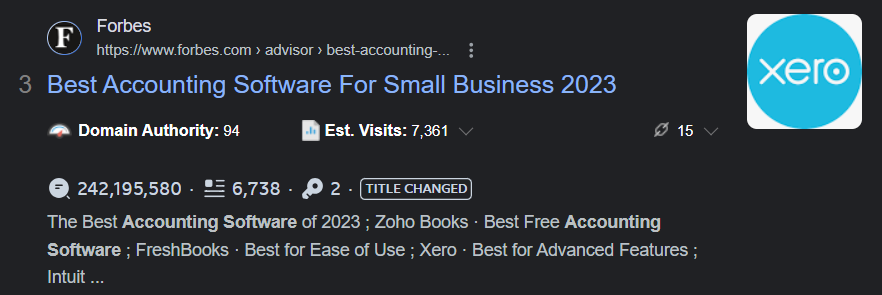
The highlighted terms in the search results show how these results associate with your search term or keyword.
1.2. Use Keyword Research Tools
Use keyword research tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, Moz Keyword Explorer, or WordStream to analyze and refine your initial keyword list.
Keyword research tools provide data on keyword popularity, competition, and search volume so you can find the best keywords and phrases to focus on.
Typically, you should target keywords with good search volume but relatively low competition because such keywords are easier to rank for. Long-tail keywords often fit this profile.
Filter out overly broad keywords or highly competitive keywords that are hard to rank for.
1.3. Integrate Keywords into Site Content
To fully capitalize on your target keywords for SEO, you need to seamlessly integrate keywords into your website content naturally.
When adding keywords to your pages, remember quality is more important than quantity. Keyword stuffing or overloading your content with keywords will hurt your rankings rather than help.
Google’s algorithms can detect unnaturally high keyword density and may penalize your pages. So, never stuff keywords in your content unnaturally or use too many of them. Apart from ranking, it also impacts content readability and user experience.
Focus on using keywords naturally throughout your copy. Aim to incorporate target terms in places where search engines look when analyzing relevance, like:
- Page titles and headers (but avoid going overboard)
- Image file names and alt text
- The first 100 words of the main content
- Subheadings spaced regularly through articles
- URL slugs
- Meta descriptions
Thoughtful placement of keywords allows search engines to associate your content with those keywords. Besides, the text reads normally to human visitors without awkward repetition or keyword stuffing.
The result is pages that rank better because search engines recognize them as highly relevant for those specific terms. It, in turn, brings more qualified traffic to your site.
2. SEO Principle: Enhance User Experience for Desktop and Mobile
Creating an excellent user experience (UX) on your website does more than just make visitors happy. It also signals search engines like Google that your content is engaging and valuable. When site visitors spend more time interacting with your pages, called increased dwell time, Google sees it as a sign of relevance.
So, optimizing for user experience for desktop and mobile devices directly improves your SEO rankings. Focus on useful, easy-to-consume content, intuitive navigation, fast load speeds, and simple design.

Meeting user needs through your website experience means higher dwell time, more return visitors, and better search engine results. Delivering quality UX is a win-win for visitors and SEO.
2.1. Improve Page Speed
In today’s world of instant gratification, slow page load times are a surefire way to frustrate users. Google analysis survey reveals:
- 53% of people expect pages to load in 3 seconds or less
- 1 out of 2 people expect a website to load in less than 2 seconds
- 46% of people said waiting for pages to load on mobiles is what they dislike the most
Exceeding that threshold leads many visitors to abandon your site for competitor sites that load quickly. Thus, optimizing your page speed is crucial for delivering an excellent user experience.
You can use Google PageSpeed Insights to diagnose your site’s current desktop and mobile load performance.
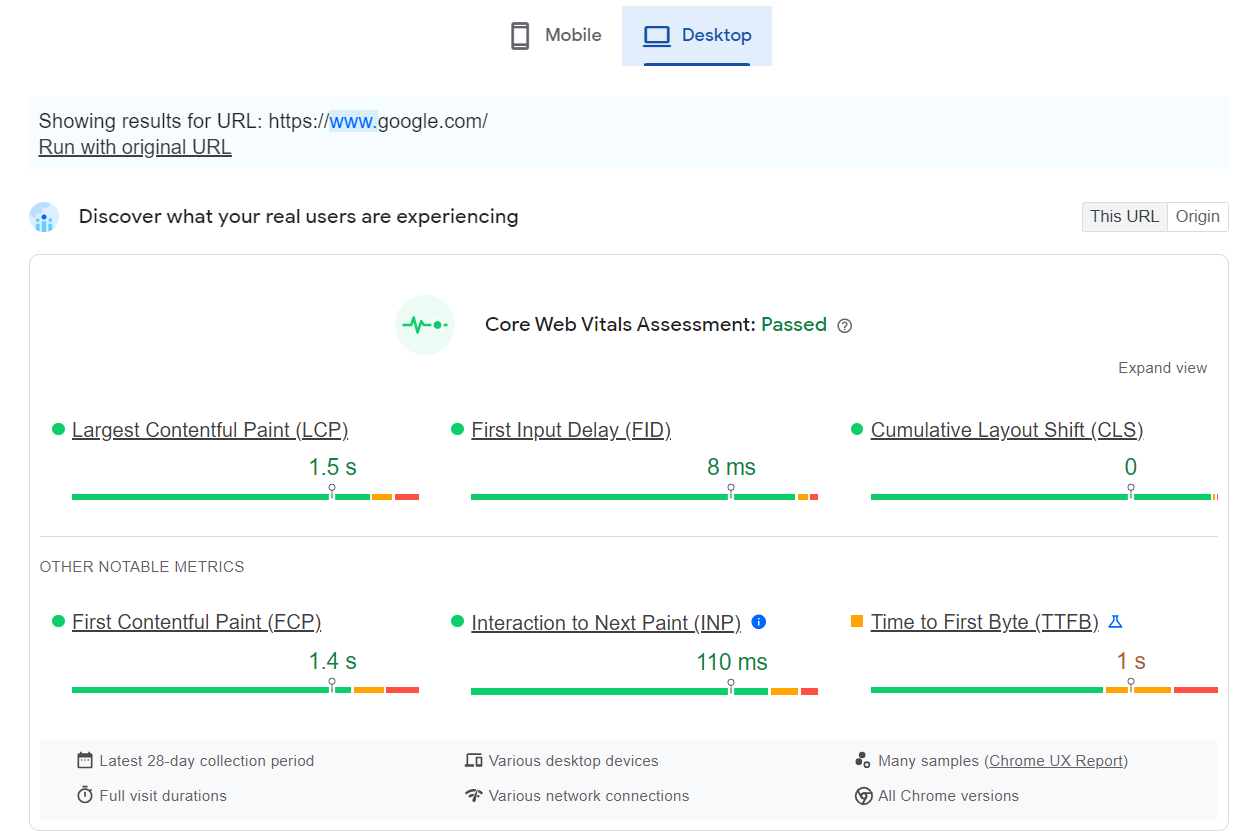
Source: Google PageSpeed Insights (Loading Speed for Desktop)
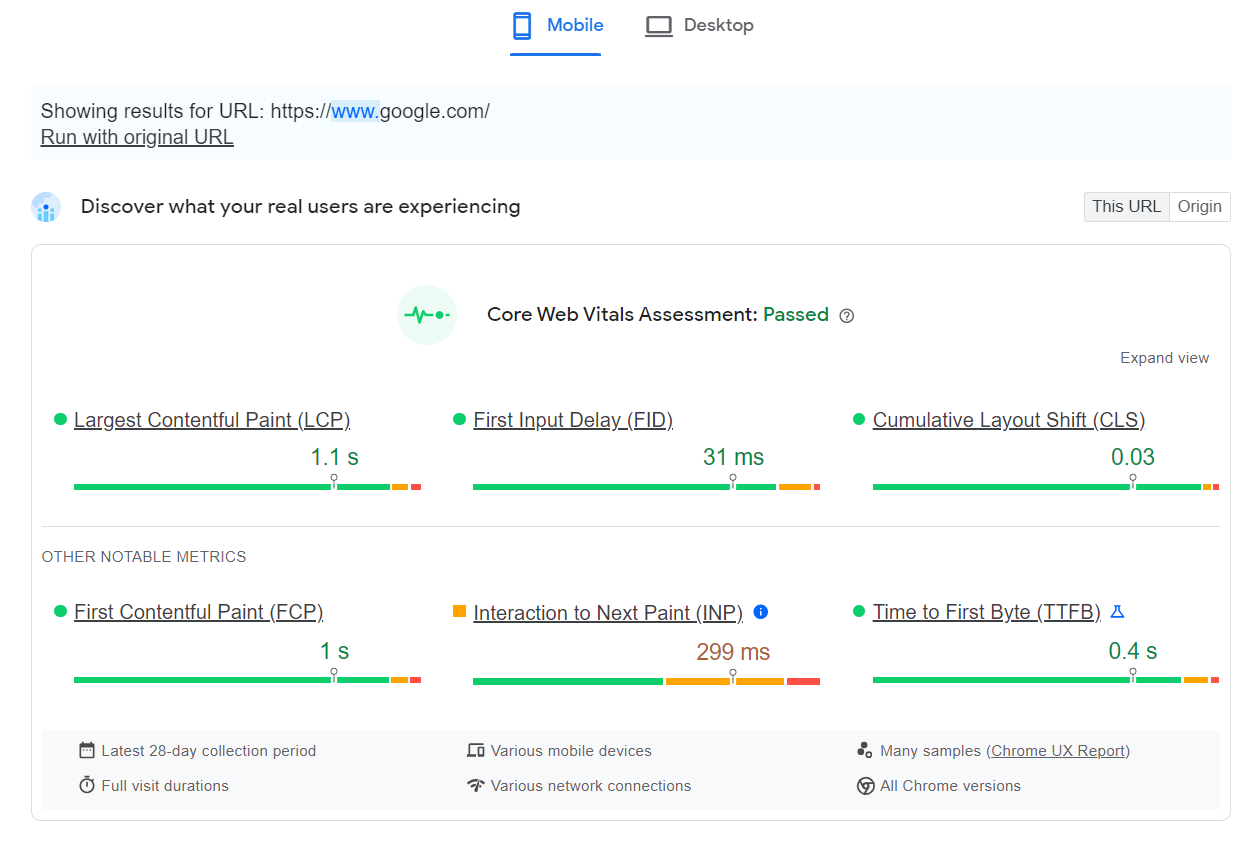
Source: Google PageSpeed Insights (Loading Speed for Mobile Devices)
To make your website load faster, you can:
- Compress images
- Enable browser caching
- Minimize redirects
- Optimize code
- Reduce overall page weight
- Upgrading to a faster web host
For more complex improvements, work with a developer to optimize database queries, leverage a content delivery network, and implement other backend enhancements.
With a fast-loading website, visitors can seamlessly access your content without delay and are more likely to be engaged and spend more time on-site.
If your website is still not improved, you can take the help of a professional digital marketing agency like Media Search Group to make your website faster.
2.2. Simplify Site Navigation
A website’s navigation design can make or break the user experience. An intuitive navigation allows visitors to find what they need easily. When structuring your navigation menu, start with broad, descriptive category labels that organize your overall content.
For example, an e-commerce site might have top-level navigation options like “Shop”, “Brands”, and “Blog”. Then, create more specific dropdowns or subcategories to direct users to deeper pages. The “Shop” menu could have sub-navigation links for categories like “Clothing”, “Shoes”, and “Accessories”.
Another good example of great website site navigation is BathTrends. The image below shows that it is quite easy to find what a customer is looking for.
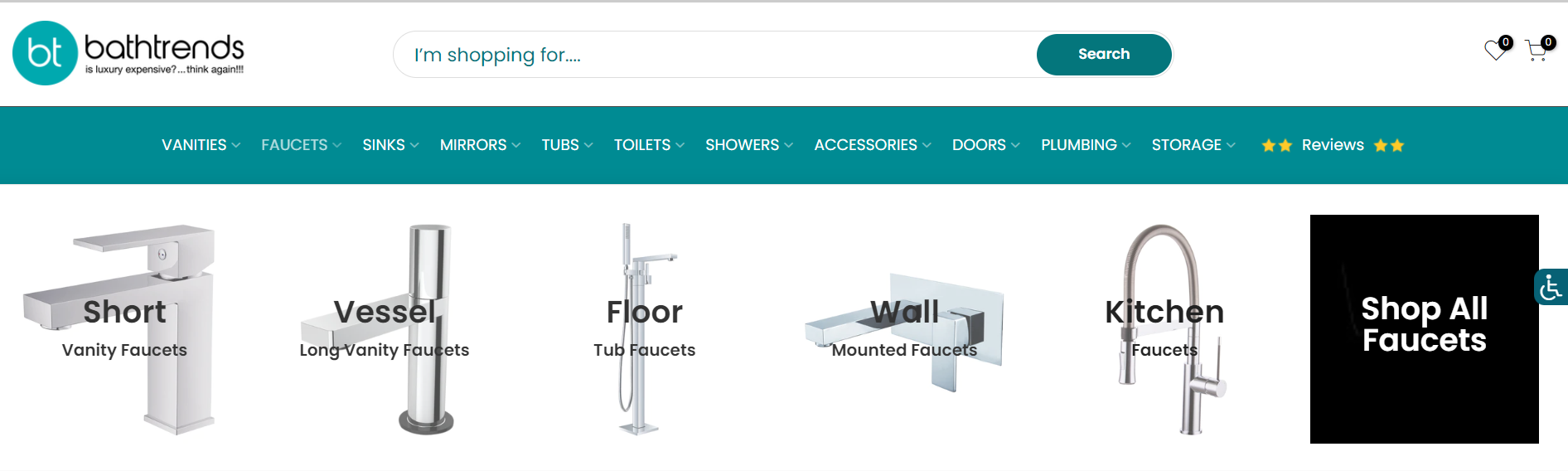
Suppose a customer wants to buy bathroom faucets. On this brand’s website, a customer can directly see faucets on the top and then choose the type they prefer or simply explore all the categories to find the best fit within a few clicks.
Test your site navigation with user research. Observe real people attempting to find pages and note any confusion. Refine based on feedback to remove pain points.
Finding the right balance of breadth versus depth takes trial and error. Too many nested submenus create complexity. Strive for clear, straightforward paths to key content areas.
2.3. Add Quality Images and Videos
Visually appealing websites capture and hold user attention better than walls of text.
With compelling visual content, you can:
- Hold visitor attention
- Enhance understanding
- Deliver an enjoyable UX
Take advantage of photos, videos, illustrations, icons, animations, and infographics to create an engaging user experience.
- Photography brings life to your pages and shows real products, people, and places.
- Videos efficiently convey information while being entertaining and shareable.
- Original graphics and illustrations showcase your brand personality.
- Infographics simplify complex data into bitesize visual nuggets.
- Icons make navigation and call-to-action buttons more intuitive.
- Subtle animations add flair without distraction.
Images are more important, especially for businesses where experiences matter. For example, tour agencies, e-commerce stores, hospitality businesses, real estate agents, etc.
A good example of appealing visuals on a website is Gulf Tours. Even if their images are small, they are clearly visible, have quality, and are enticing.
When users arrive at a page, visuals draw the eye and break up long blocks of copy. It improves skimmability for quick content consumption. People are also more likely to remember key information presented visually.
2.4. Monitor Core Web Vitals
Google’s Core Web Vitals provide key metrics for assessing user experience. Optimizing for web vitals can directly improve your website’s performance.
The Core Web Vitals are:
- First Input Delay (FID) – measures interactivity by timing the first time a user can click on your page. Aim for under 100 milliseconds.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) – gauges loading experience by timing when main content loads visually. Keep it under 2.5 seconds.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – tracks visual stability by quantifying unexpected layout changes. Minimize shifts and maintain CLS under 0.1.
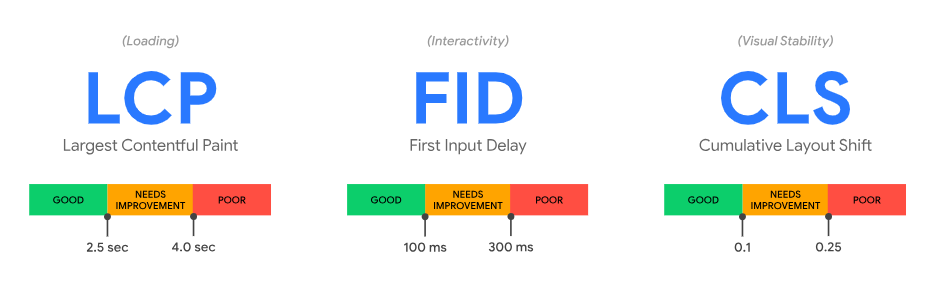
Check your current Core Vitals scores in Google Search Console and then work to optimize pages with poor ratings.
To improve FID:
- Reduce JS execution times
- Enable caching, compress images
- Simplify page design to improve FID
To optimize LCP:
- Minimize render-blocking resources
To optimize CLS:
- Avoid late-loading elements
- Use relative sizing for images/text
Tuning your site for excellent Core Web Vitals scores directly enhances user experience. And since they factor into Google rankings, core web vitals optimization also improves your SEO.
3. SEO Principle: On-Page SEO
3.1. Optimize Title Tags
A title tag tells search engines and users what a specific page is about. Optimizing your title tags is a crucial on-page SEO tactic.
It is a good practice to use target keywords at the start of titles if possible. This helps search engines understand the page’s focus and makes it more appealing in results.
For example, a title for a dog training business could be “Portland Dog Training: Obedience Classes and Private Lessons.”
Keep titles concise but descriptive – aim for around 60 characters or 580 px. Summarize the page’s purpose and highlight key information.
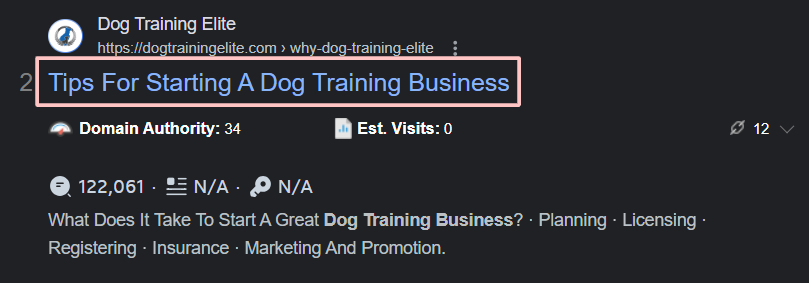
Avoid duplicating the same title across multiple pages. For better rankings, you must create unique, relevant titles for each piece of content.
You can tweak titles over time to improve click-through rates from search results. Try different keyword placement or add power words like “tips”, “guides” or “secrets”.
An eye-catching, keyword-optimized title tag signals search engines that your content is valuable for that topic. It also encourages users to click through to your page instead of competitors. Optimizing your titles for relevance and engagement is a smart SEO practice.
3.2. Optimize Meta Descriptions
The next thing you need to optimize after titles is meta description. The meta description gives search engines and users a summary of what a page is about. It is also shown as a snippet under the title tag in search results. An optimized description can improve click-through rates.
Keep meta descriptions between 150-160 characters or 920 px – the ideal length before Google truncates them. Summarize the page’s unique value proposition. Include a relevant keyword phrase if it fits naturally.
For example, a meta description for a page about SEO tips could state: “Our complete guide to SEO provides actionable tips to boost your organic search traffic through keyword research, link building, site optimization, and more.”
Avoid simply repeating the title tag content. Write descriptively to entice searchers. Use compelling wording and highlight benefits.
While meta descriptions don’t directly impact search rankings, they influence click-through rates. An informative, engaging description gives users a reason to visit your page over competitors.
3.3. Optimize Images and Alt Text
Images make content more engaging for users. With proper optimization, they also boost on-page SEO.
Use descriptive file names containing target keywords, like “rose_flower.jpg”. It gives search engines hints about the image content.
Fill out the alt text and title attributes for each image. The alt text appears when images don’t load and is read by screen readers for accessibility. Well-written alt text includes keywords while still being natural.
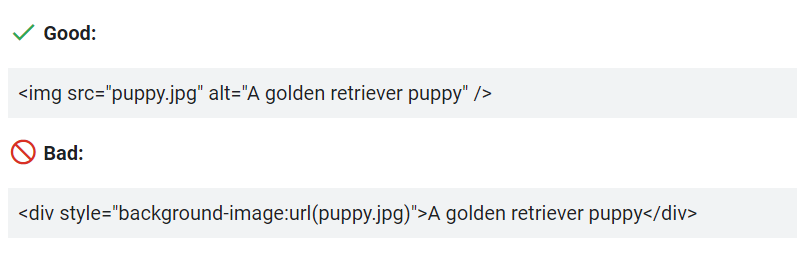
Source: Google Search Central (Google Image SEO Best Practices)
Ensure you compress images so that their file size is reduced and the quality is also not compromised. Smaller image files lead to faster load times. JPEGs tend to compress better than PNGs. So, prefer JPEG images.
Include images relevant to the page content to reinforce the topic visually. Insert them throughout the content to break up the text.
Why Optimize Images on Your Websites?
- Properly optimized images reinforce page relevance for keywords.
- Optimized images also enhance the user experience.
- They add visual interest, accessibility, and valuable cues for search engine crawlers.
- Images bring pages to life while boosting SEO.
3.4. Include Header Tags (H1, H2, and H3 tags) in Your Content
Header tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) are HTML elements that make text stand out on a page. They help structure content and signal importance to users and search engines.
- Place target keywords in relevant header tags throughout a page’s content.
- An H1 contains the main page keyword.
- H2s and H3s include secondary keywords and subtopics.
For example:
H1: Social Media Marketing Tips
H2: Develop Your Brand’s Voice
H3: Post Engaging Content
H3: Use Visual Media
H2: Promote Your Accounts
H3: Leverage Cross-Promotion
H3: Run Contests & Sweepstakes
Header tags break up blocks of text and outline the content for better immobility. They also emphasize keywords so search engines better understand page relevance.
Strategic use of properly structured header tags improves on-page SEO while enhancing the user experience.
4. SEO Principle: Content Optimization
4.1. Topic Research
Start by using keyword research tools to uncover topics and terms with sufficient search volume and reasonable competition. It helps ensure there is audience interest and opportunity to rank.
Look at questions people are already asking around your target keywords to identify knowledge gaps your content can fill.
Analyze top-ranking competitors for topic ideas and insights into user intent. Explore resources like Quora, Reddit, online forums, and influencer content to discover additional facets of a topic.
When researching topics for your website, ensure that the keywords you target and the topics you choose are related to your business.
Suppose you are an AC repair company, and you see that many people are searching for the best landscaping design. If you write a blog post about this topic, our website may get higher traffic than before. However, you will not gain any leads, customers, or revenue. This is because people searching for landscaping ideas are not going to hire an air conditioner company.
So, it is a must that you choose the right keywords that bring in relevant traffic and leads.
4.2. Content Creation
With your outline as a guide, write content that provides comprehensive value for your keyword targets. For content creation, try different content formats, such as:
- Blogs
- Articles
- Videos
- Infographics
- Guides
- E-Books
Seamlessly incorporate keywords throughout your content using headings, subheadings, meta descriptions, image alt text, URLs, and bolded in-text mentions. But avoid awkward stuffing of keywords.
- Keep sentences concise and paragraphs short for better readability.
- Break up text with relevant images, infographics, videos, and quotes.
- Use tools like Grammarly and Hemingway Editor to refine your writing.
- Use Duplichecker or other plagiarism checker tools to identify and remove duplicate content.
- Insert links to related content to develop keyword clusters.
Promote your content upon publication through social media, outreach for backlinks, and internal cross-linking. Track analytics to identify opportunities for refinement.
Performing diligent research and writing engaging and optimized content is one of the key strategies to ensure SEO success.
5. SEO Principle: Technical SEO
Technical optimization makes your site more search engine friendly so pages can be crawled, indexed and ranked properly. Here are key areas to focus on:
5.1. Optimize Site Structure
A website’s information architecture impacts how easily search engines can crawl and index its pages. Follow these tips to optimize site structure:
- Design intuitive navigation so that site visitors can quickly find what they are looking for. Use clear menu labels, site search, and breadcrumb trails.
- Interlink internal pages through contextual links in content and site menus. It helps crawlers discover new or updated content.
- Organize your site into logical, hierarchical categories centred on topics.
- Keep the homepage focused on the overarching site purpose. Create subcategories for additional pages.
Avoid burying content too deep. Try to limit page depth to 3 or 4 layers.
Create an XML sitemap listing all pages to be indexed. Upload this to your site and register it with Google Search Console to improve page discoverability.
An optimized site structure streamlines user journeys and makes crawling more efficient. By designing an intuitive architecture and enhancing internal linking, you ensure search engines can fully index your content for better rankings and visibility.
5.2. Make Your Pages Indexable
Search engines need to access a page’s code to crawl and index it. Thus, you need to ensure that your web pages can be easily indexed and crawled by search engines.
To make your pages indexable, you need to:
- Ensure correct server settings to allow indexing and enable directory browsing for URLs.
- Avoid restrictive robots.txt files or iframes.
- Check for noindex meta tags that are mistakenly added.
- Verify pages to ensure that they are fully indexable and can be discovered easily.
5.3. Make Your Website Easy to Crawl
Search engine crawlers follow links to discover new content.
To make your website crawlable, you should:
- Link your website pages internally using contextual text links and site-wide navigation.
- Limit site hierarchy with a maximum of 3-4 levels for better accessibility.
- Use sitemaps to outline your URL structure.
Optimizing crawlability helps search bots fully explore your content.
5.4. Check Robots.Txt File
The robots.txt file gives crawling instructions. Avoid restrictive settings that block bots from key pages.
Disallow irrelevant directories and test your robots.txt using online tools to spot errors that prevent indexing. Proper robots.txt settings allow helpful bots while screening scrapers and bad bots.
Also, submit your sitemap here for faster discovery.
Important Note: Do not use robots.txt file to hide webpages from Google search results. If you want to hide certain pages, you must use noindex.
5.5. Pages with No Index
The noindex meta tag blocks indexing. Review where you have used no index tags to ensure high-quality pages aren’t mistakenly noindexed. This can happen with 5xx error pages or outdated content that has not yet been removed.
For pages that need to be hidden, use “noindex, follow” to retain internal linking value. It is a good practice to manage noindex tags proactively to prevent the loss of good pages.
To prevent all search engines from indexing your site, you can use the following code:
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”>
To prevent only Google Search from indexing your site, you can use the following code:
<meta name=”googlebot” content=”noindex”>
5.6. Verify Sitemap
A sitemap lists your URL structure for search engines. However, just having one isn’t enough. Verify your sitemap is submitted to Google Search Console for crawler access.
According to Google Search Central, here is a basic XML sitemap containing the location of a single URL:
<?xml version=”1.0″ encoding=”UTF-8″?>
<urlset xmlns=”http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9″>
<url>
<loc>https://www.example.com/foo.html</loc>
<lastmod>2022-06-04</lastmod>
</url>
</urlset>
For complex sitemaps, you can visit sitemaps.org.
After creating a sitemap, submit it to the Google Search Console.
Check for indexing errors that are blocking the pages listed. Refresh sitemaps regularly as you add new content and pages to your website.
Sitemaps aid discovery but still require verification for full SEO benefit.
6. SEO Principle: Off-Page SEO
6.1. Internal Linking
Internal links between pages on your site are a key off-page SEO tactic. Here are tips for using internal links to boost rankings.
Internal links allow pages to pass “link equity” to each other. A page with numerous quality backlinks can share its power by linking internally.
This raises the authority of pages with fewer external links. So, adding contextual internal links helps less popular pages rank better. Link relevant pages using anchor text keywords where appropriate, as shown in the image.
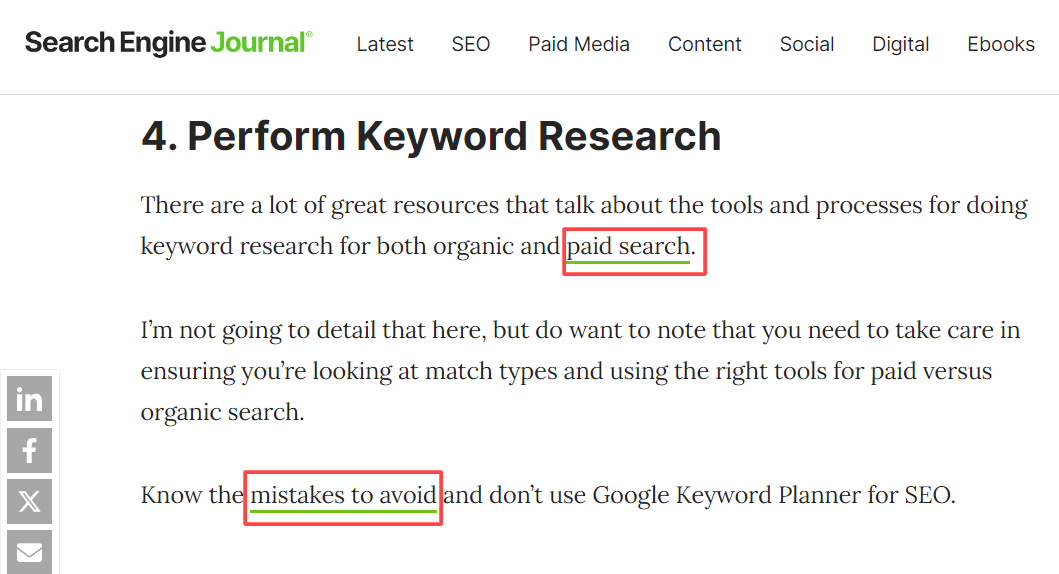
It also enables new or updated content to gain rankings faster by piggybacking on established pages. Smart internal linking amplifies your overall domain authority.
6.2. Strategies for Effective Internal Linking
- Cross-link blog posts on similar topics to develop clusters around keywords. For example, link each SEO tips post to others.
- Link important pages like “About” or “Contact” from higher-traffic pages for visibility.
- Add links within on-page content where useful, not just within menus and sidebars.
- Use descriptive anchor text, not repetitive generic phrases like “click here” or “read more”.
- Install WordPress plugins to automate internal linking suggestions during content creation.
Analyze internal linking patterns using site crawl tools. Identify orphaned pages that lack internal link juice. Assess which pages accumulate the most internal links to inform link-building priorities. Continue adding relevant links and monitor their impact using Google Search Console.
6.3. Earn Backlinks
Backlinks from external sites are a major ranking factor because they signal authority and relevance. Earning authoritative backlinks should be a priority.
Start by identifying websites, blogs, and resources that overlap with your industry and target audience. Look for sites with high domain authority and quality content.
You can use a tool, such as Ahrefs, to check your website’s backlink profile. All you need is to visit Ahrefs backlink checker and enter the URL of your website.
For example, we entered the URL of Investopedia, and the result is shown in the image.
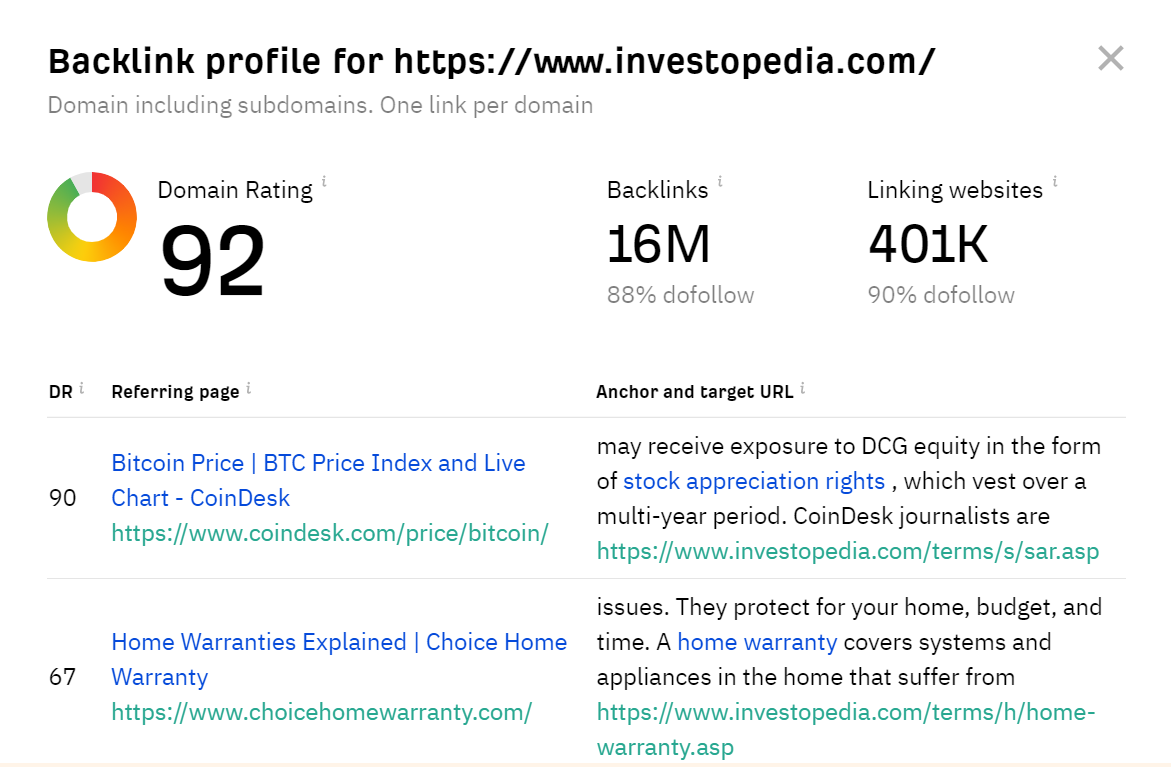
Source: Ahrefs
Outreach these sites about contributing a relevant guest post with a contextual backlink. Don’t spam! Pitch thoughtfully and provide value.
Look for link roundups and lists like “top blogs” or “best tools” in your field where you can apply to be included.
Having a diverse backlink profile with links from widely trusted sites helps lift your own domain’s authority for better SEO.
6.4. Social Share
Social sharing is a great way to earn backlinks that point to your website. Here are some of the tips you can try to build links through social sharing:
- Share your new posts on relevant LinkedIn Groups and Quora Spaces.
- Engage followers on Twitter with content teasers, polls and questions.
- Use high-quality visuals on Instagram and Pinterest to drive organic engagement.
- Make shareable PDF guides, tools or resources related to your content and promote them on SlideShare.
- Use YouTube to host webinars, behind-the-scenes and instructional videos.
- Podcast interviews are an engaging audio format that can yield backlinks.
Interact meaningfully with others’ content instead of just self-promoting. Comment on blogs, share others’ posts and engage the community. This raises your visibility and credibility for potential backlinks.
Monitor click-throughs from social shares back to your site using UTM tracking codes. Pay attention to which platforms and content types perform best. Keep diversifying your outreach for ongoing improvements.
7. SEO Principle: Analytics Tracking to Monitor SEO Performance
Analytics tracking is crucial to know whether your search engine optimization efforts yield any results or not. Remember only one thing “if you can’t measure it, you can’t treasure it”. So, when you want to gain and improve SEO results, it is important to measure the key metrics right from the beginning and see any improvements.
7.1. Key SEO Metrics to Track
- Clicks and Impressions
- Organic traffic
- Keyword rankings
- Referring domains
- Indexed Pages
- Core Web Vitals
- Bounce rate
- Exit rate
- Pages per session
- Average session duration
- Organic traffic conversions
- Top Queries
7.2. SEO Tools to Track SEO Performance
- Google Analytics
- Google Search Console
- Ahrefs
- Semrush
- Screaming Frog
For example, using Google Search Console, you can track different metrics that determine SEO performance easily.
7.3. How to Track SEO Performance
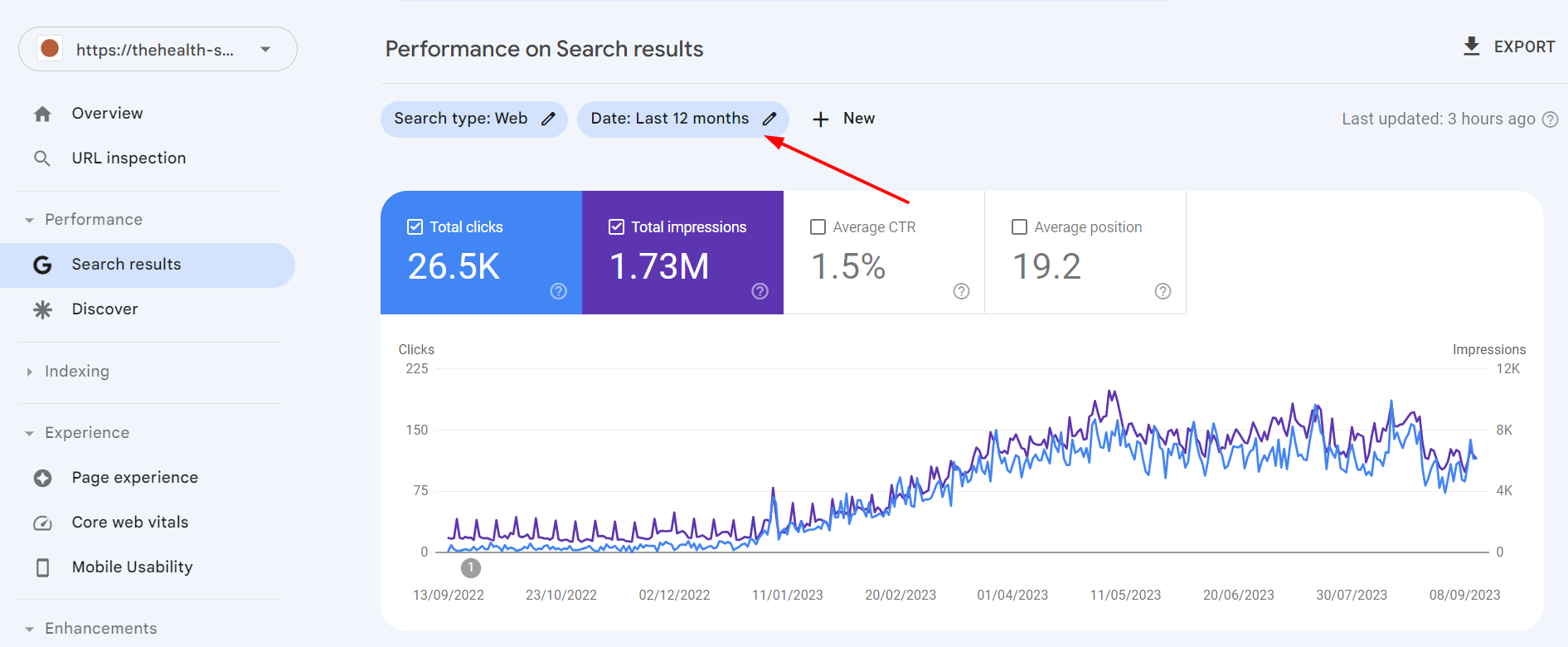
Go to Google Search Console and click on the Performance tab to see how your website is performing.
Also, explore other metrics, such as CTR, average position, page experience, core web vitals, etc.
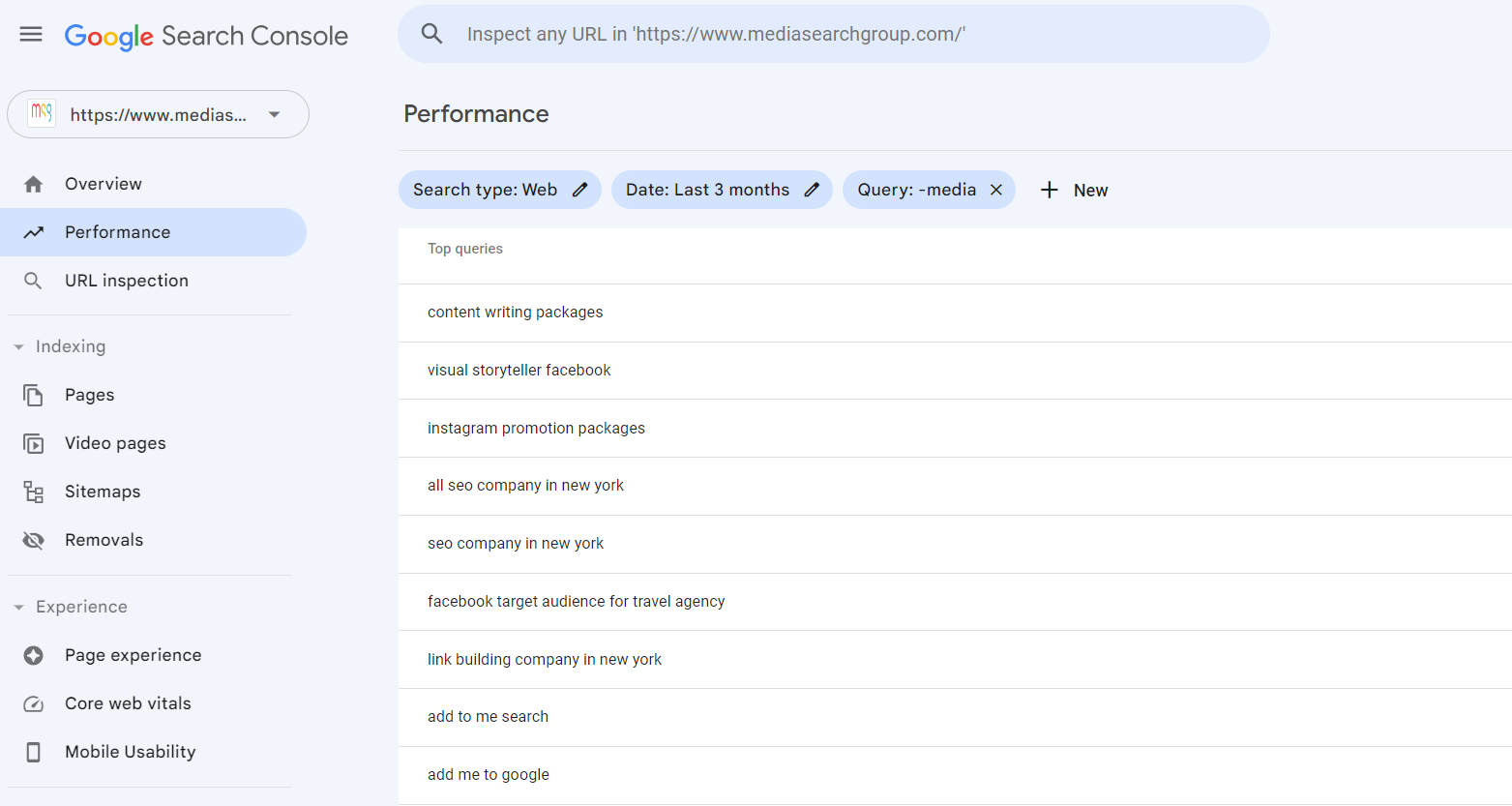
Checking top queries is also a good way to find out what your targeted customers search for online and create relevant content.
Conclusion
SEO is a successful digital marketing technique as SEO leads are found to have a 14.6% close rate, which is 8.5 times higher than outbound leads. So, don’t delay anymore and make a strong online presence using the above core SEO principles.
If you find it difficult to manage the SEO of your website, get professional help from a reputable SEO company that serves your area and offers comprehensive SEO solutions within your budget.
Latest posts by Vijaya Tyagi (see all)
How To Track Shopify SEO Performance & Metrics (2025) - January 14, 2025
Link Building Strategies: The Ultimate Techniques for 2025 - December 31, 2024

