Google Featured Snippets Updates You Must Know About
Recently updated: February 15th, 2025
Google is always on this constant journey of improvement and providing consumers the best search experience. Consequently, it rolls out updates now and then to serve its users in a much better way. However, its updates also affect the overall ranking of websites and, thereby cause chaos in the SEO and marketing world as they aim to win the spot on the first position or at least on Google’s first page.
Today, we are going to discuss Google Featured Snippets and how recent updates affected them.
Before we jump to details, let’s learn what exactly featured snippets mean.
What are Featured Snippets?
A Featured Snippet is a brief extract or cuts out a piece of information, deemed to be the best answer to your query by the search engine algorithm. Featured Snippets appear on the top, even above the first ranked URL. Therefore, Featured Snippets were usually referred to as Rank Zero.
The sole purpose of search engines for displaying Featured Snippets is to help people find the answer to their query with utmost ease and save their time.
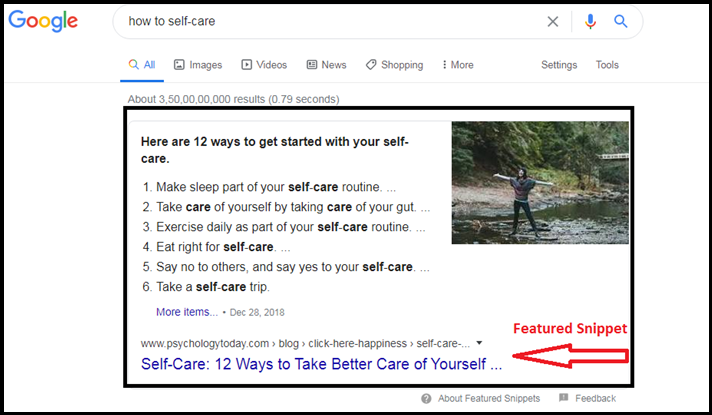
When you enter a query and hit the search button, you will see a couple of things in the Featured Snippet.
- Right below the search bar, there is a box that contains the answer that Google believes to be the most suitable for your query. This is called a Featured Snippet.
- The Featured Snippet includes the title of the article in which the answer was found and the URL of the website on which the article is present.
- The URL of the Featured Snippet is not the same as the first organically ranked link (though it might not be the case in some cases).
In general, there are three types of Featured Snippets that vary based on the query.
- Paragraph
- List
- Table
80% of the featured snippets are paragraph snippets, with lists and tables displaying on 10% and 7% of searches, respectively.
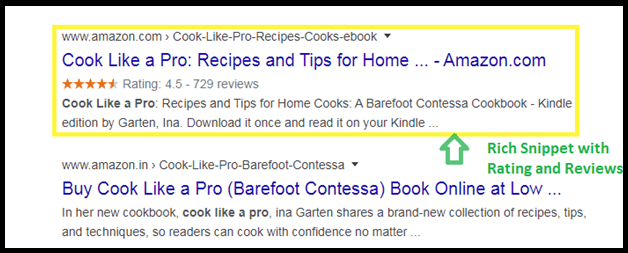
Note that Featured Snippets and Rich Snippets are different. While Featured Snippets appear on the top above the first organic search result, Rich Snippets are normal Google Search results with additional data. The additional data is extracted from Structured Data found in the HTML of a web page. The most common Rich Snippet Types are reviews, recipes, and events.
Now that you are familiar with the concept of Featured Snippets, let’s learn the latest developments in the Featured Snippets made by Google.
Latest Google’s Updates to Featured Snippets
- The January 2020 Featured Snippet Update
For many years, capturing Featured Snippets has been the goal of SEO services as they add to the organic traffic and provides the highest visible spot. Featured Snippets are often considered in various SEO packages due to their potential in improving search rankings.
According to a Moz report prepared by Britney Muller, Senior SEO Scientist, 24% of SERPs display a featured snippet.
However, the Featured Snippet update rolled out by Google in January has affected the value of earning rank zero position.
Earlier, websites benefited from being displayed in the spot of Featured Snippet in two ways:
- First, in the Featured Snippet Result itself
- Second, in the Organic Search Result, usually among the top several results
So, there were higher possibilities of earning clicks.
Now, Google de-duplicates these results. It means, for a given query, a URL would either appear as a Featured Snippet or in the organic results, but not both.
The January 2020 Featured Snippet Update was rolled out to de-clutter the results, meaning the Featured Snippet that was previously considered Rank Zero is now seen as Rank 1 on the SERP. The Featured Snippet Web Page/URL may appear a second time on Page 2 of Google, but there is no guarantee.
Thus, not being able to rank at both places could lead to potential traffic loss.
According to the Study of 2 Million Featured Snippets conducted by the Ahrefs, when a Featured Snippet appears, it gets only ~8.6% of clicks, while the page that ranks below the Featured Snippet gets ~19.6% of clicks.
On the other hand, in a search result page with no Featured Snippet, the first result gets ~26% of all clicks.
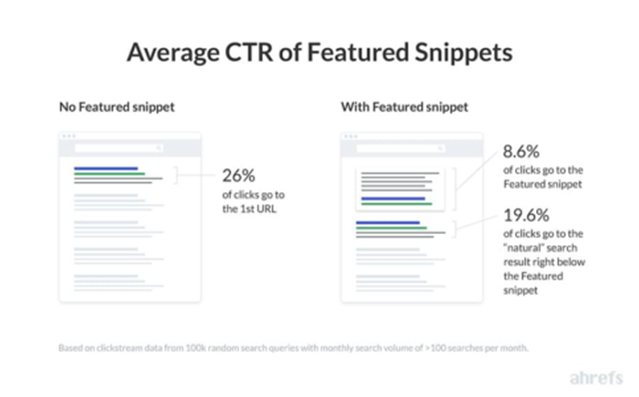
Image Source: Search Engine Journal
Therefore, appearing in the Featured Snippet may or may not be satisfactory for website owners these days.
But if you take a look at the research report by SEOClarity, they didn’t notice any major fluctuation in the traffic to Featured Snippet URLs because of this update.
Also, note that Featured Snippets come with an added advantage that their content is often read aloud by smart Google voice search devices.
- Right Sidebar Featured Snippets
Another recent development is related to the featured snippets that appear on the right sidebar of SERPs on desktop devices. They seem just like Knowledge Panels. Along with the January 2020 Featured Snippet Update, Google announced that it will soon be folding the right sidebar featured snippets into the main panel of search results. The goal is the same – de-duplication.
Before de-duplication
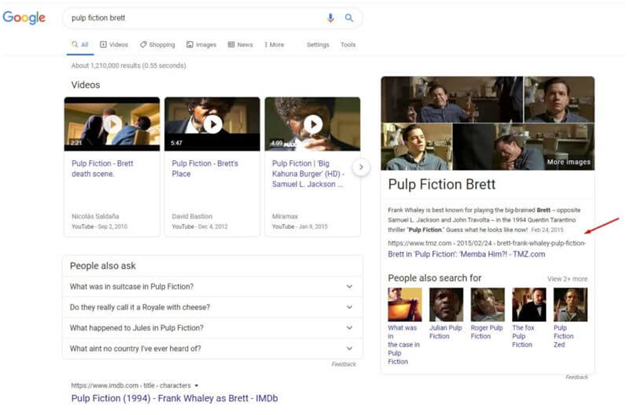
Image Source: Search Engine Land
After de-duplication
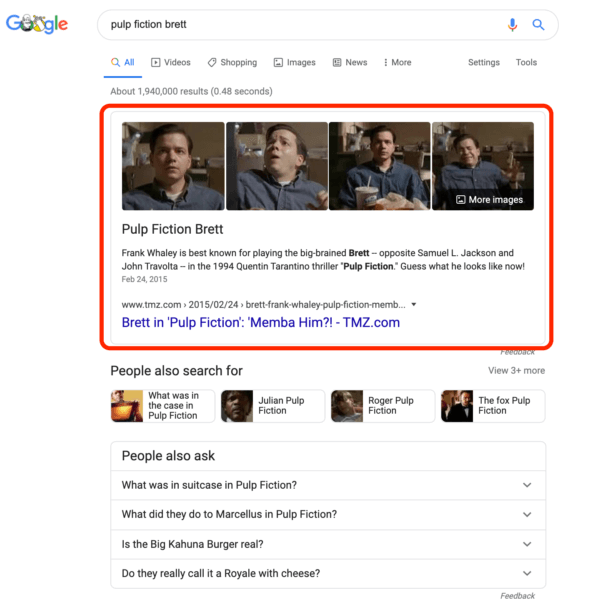
Image Source: Search Engine Land
- BERT Update for Featured Snippets in 70 Languages
Google rolled out the BERT update on December 9, 2019. BERT is referred to as Google’s neural network-based technology for natural language processing (NLP) pre-training. BERT is an acronym for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers. Though the update already existed for the English language, Google introduced it in 70 languages in December.
This technique helps a machine better understand the meaning of words in a query along with the nuance of context. The most important thing here is to understand that BERT analyzes the query and not the web page.
But, still, it makes an impact on the Featured Snippet results. The reason behind this is the same fact that BERT helps in understanding and analyzing what actually query means based on the surrounding context. So, what meaning will be perceived by BERT will affect what answer would be considered the best for that query.
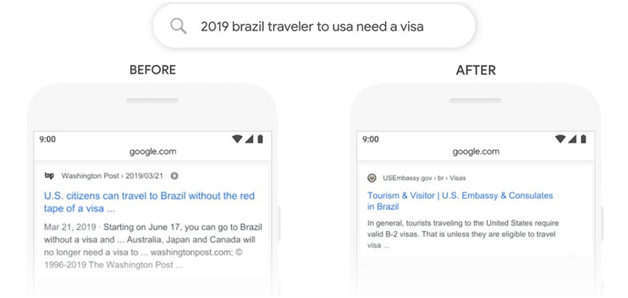
Image Source: WordStream
- Carousel Snippets Continue to Prevail
Also known as Bubble Refinements, Carousel Snippets were launched in 2018 but still, they are prevalent in the SERPs. According to Moz BI Analyst, Eric Hedekar, after parsing over 1.4million featured snippet SERPs, they found every 13th of them had a carousel of refinement bubbles. Though it is not much common, it is as common as Table Formatted Featured Snippets.
These snippets are the reflection of users’ ability to refine their search based on commonly-used modifiers related to the original query. These modifiers often include competitor names, locations, product attributes, and so on. Besides, they also allow the URLs to own the Featured Snippet at the same time.
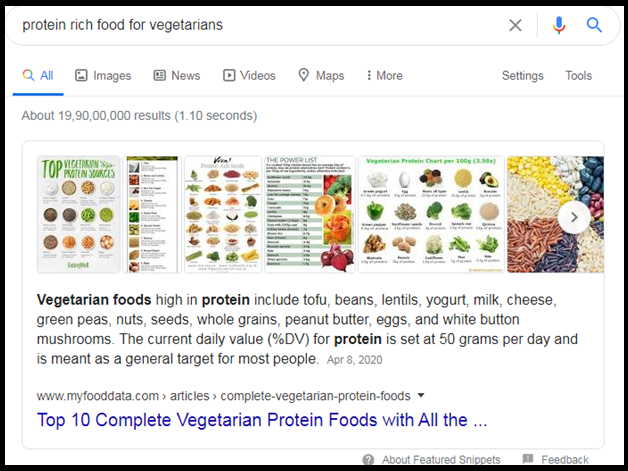
In the above image, one can clearly notice that the query contains two different attributes – protein-rich and for vegetarians. Both these attributes played a role in refining the search and providing the context to query “food”. Plus, even with the Carousel Refinement Bubble, the URL owned the Featured Snippet.
- TargetText – Featured Snippet on the Page Now Appears in Yellow Background
targetText is the fragment of the content of Featured Snippet URL used by the Chrome Browser. Last year, SEO experts found out that textTarget functionality was being applied to Featured Snippets and also indicated that this feature works even for hidden content.
The recent development announced by Google in June 2020 is that clicking on featured snippets now takes users to the exact highlighted text for HTML pages wherever they can confidently determine where the text is.
As we have done with AMP pages since December 2018, clicking on a featured snippet now takes users to the exact text highlighted for HTML pages, when we can confidently determine where the text is, for browsers that support the underlying technology….
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) June 3, 2020
It means when you click on the Featured Snippet URL directly, the selected fragment of text on the page is highlighted with a yellow background.
For better clarity, check out what Google displayed for the query “What is Featured Snippet?”
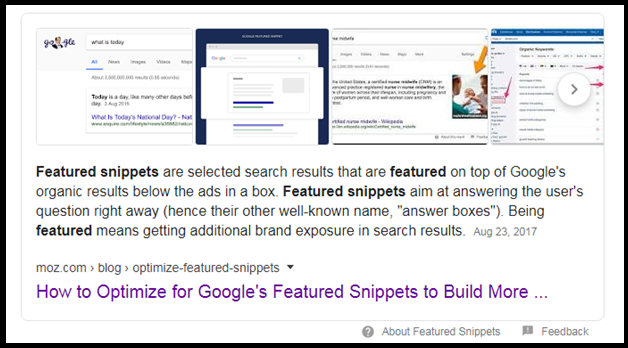
When we clicked on the link shown in the featured snippet, see how the chosen content is highlighted.
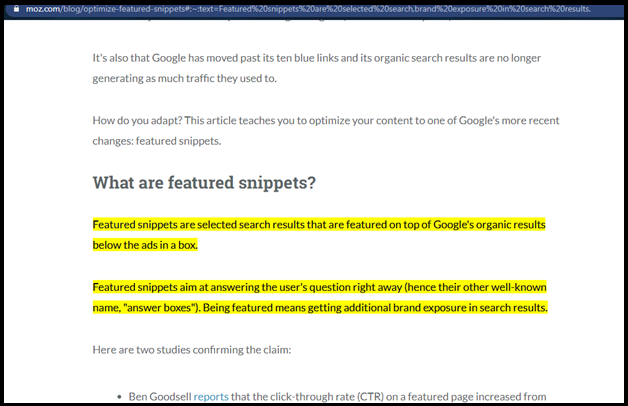
Another interesting thing to note in these images is that the URL is also changed and contains additional parameters.
It seems that what made the text highlighted is:
#:~:text=
You can recreate the effect on your web pages as well. Add this URL parameter to your web page URL. After the “=” sign, add words you want to highlight from that page. Hit enter. Those words will then display as highlighted text.
How to Prevent Content from Appearing in Featured Snippets
Google facilitates three ways to help you avoid the content from being displayed in Featured Snippets.
- Nosnippet – Add nosnippet Meta Tag to the web page to prevent content from appearing in featured as well as regular snippets (Meta descriptions).
- Data-nosnippet – To prevent specific text from appearing in snippets anywhere, apply data-nosnippet tag inline with the span, div, or section HTML elements.
- Max-snippet – Try max-snippet tag to prevent content from appearing in only Featured Snippets (and not the regular snippets).
Do the concepts of E-A-T and YMYL affect Featured Snippets?
Google is paying attention to the quality of content within organic search results by giving more preference to the content that is produced by subject matter experts, have authority, and can be trusted.
Besides, it also now scrutinizes sites that fall under the category of “Your Money or Your Life”.
So, it is interesting to see whether both these concepts make any impact on the Featured Snippets.
First, you need to know that there is already a set of requirements that decides which text will appear in the snippet.
The content in the featured snippets must not be sexually explicit, hateful, violent, dangerous, harmful, or contradict consensus on topics related to public interests.
Based on these criteria, Google can remove the featured snippets and people can also report for violating policies.
When it comes to controversial topics, different search engines show the results differently.
For instance, Bing rolled out a feature to handle controversial queries, known as multi-perspective answers so that it can show both sides of the story that doesn’t have a single answer. On the other hand, Google shows only one perspective.
According to a study conducted by Search Engine Journal, for even more controversial queries, Google is simply choosing to display no featured snippet, while Bing is more likely to display a featured snippet that takes one side of the argument. In this case, Bing didn’t display multi-perspective answers.
In case of YMYL queries, 78% of YMYL Featured Snippet Results that earned readability scores of B-E (on the scale of A to E, where A means higher readability and B means poor readability), the content of featured snippets is a bit more advanced and difficult to read when compared to the full pages from which the content was pulled. 23% of featured snippet content earned a sentiment score of neutral, while 13% of them earned negative, according to the same study conducted by Search Engine Journal.
Besides, it was found in the study that – the web pages that Google is selecting to display Featured Snippets for YMYL queries contain usually longer content (more than 1,600 words). This could be because Featured Snippets are selected from the pages that already rank on the first page of Google and exhibit good quality with longer word count to cover YMYL topics sufficiently.
Summing Up
Now that Google has changed its ways about how Featured Snippets are displayed and established the de-duplication policy, it may be time for SEO professionals to give it a thought whether they want the content of a web page to appear in the featured snippet result or not. Though there may or may not be an impact of the click-through-rate of the page, there are certainly some added benefits of having content displayed in Featured Snippets, such as content will be read aloud by smart voice search devices, the trust of people in your content might increase, and your site gains high visibility.
Latest posts by Vijaya Tyagi (see all)
What Is SEO In Digital Marketing? How Does It Work? - March 7, 2026
Top 15 Best Backlink Checker Tools for SEO 2024 - March 6, 2026